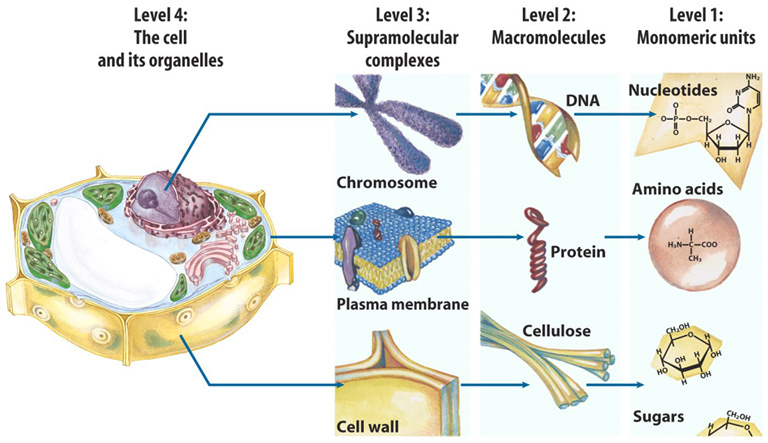
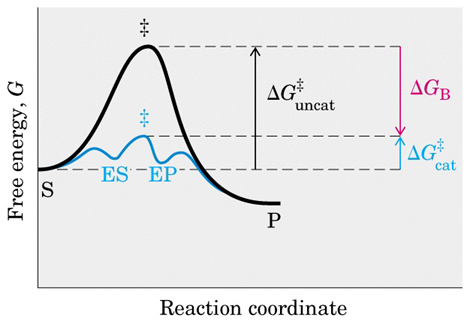
20.
Draw the peptide sequence you translated in question #19(b) in a
solution at pH 7.0. Write the pKa for each applicable group. [15 pts]
(Draw a
pentapeptide with the sequence SHGSKW). pKa values should be at the
amino- and carboxy-termini, histidine, serine and lysine which should
all be in the correct protonation state.
21. List and
describe three regulatory mechanisms that apply to enzymatic function. [3 pts]
Allosteric
modulator:
Reversible
binding of an allosteric modulator, usually at a site remote from the
active site, increases or decreases the reaction rate of an enzyme.
Feedback inhibition:
When the
end-product in a multi-step pathway is in high enough concentrations it
acts to inhibit (usually as an allosteric effector) enzymatic function
at an early step in the pathway. The effect of this is to decrease
end-product formation.
Proteolytic cleavage:
Inactive forms of enzymes (zymogens) exist in the
cell, yet are unable to catalyze reactions until activated by proteases.
22. Identify each stage of
replication and list one enzyme that functions at each step.
[6 points]
Initiation:
Helicase, gyrase, dam
methylase
Elongation: Polymerase, primase
Termination: Ligase,
topoisomerase
23. List 4
differences between DNA and RNA (describe as needed for clarity). [4
pts]
RNA has C2’-OH, DNA does not
DNA has Thymine, RNA has Uracil
DNA is composed of 2 molecules (2 independent strands) in antiparallel
orientation, whereas RNA is a single molecule.
DNA predominantly double stranded, whereas RNA has large single
stranded regions
RNA is smaller
RNA has more complex structures
DNA is nuclear, RNA is made in the nucleus and functions primarily in
the cytoplasm
Bases in RNA are often highly modified
24. List 4 types of
information stored in genomic DNA besides protein encoding genes. [4
pts]

25. Matching [15 pts]:
| a. B-form DNA |
__k__ the limiting rate of an enzyme
catalyzed reaction at saturating [S] |
| b. A-form DNA |
__e__ synthesized in the nucleus by RNA
pol III |
| c. cellulase |
__l__ conjugate acid/base forms of water
accelerates the reaction by transferring a proton |
| d. cellulose |
__h__ conjugate acid/base forms of an
amino acid side chain from the protein or other non-water group
accelerates the reaction by transferring a proton |
| e. tRNA |
__i__ the overall rate of substrate to
product conversion, also called the specificity constant |
| f. mRNA |
__f__ synthesized by DNA-dependent RNA
pol II |
| g. rRNA |
__d__ A polysaccharide composed of linear
and branched chains |
| h. general acid/base catalysis |
__n__ successive basepairs in DNA show a
rotation with respect to each other of roughly 36 deg
|
| i. kcat/Km |
__b__ rise per base 2.3 Å, 11
basepairs per turn, basepair tilt of 19deg, helix is symmetric and wider |
| j. Km |
__m__ enzymes decrease the degrees of
freedom in ternary complexes thereby enhancing the reaction rate |
| k. kcat |
__g__ synthesized in the nucleolus by RNA
pol I |
| l. specific acid/base catalysis |
__c__ an enzyme that hydrolyses the
O-glycosidic linkage between sugars in a polysaccharide |
| m. entropy reduction |
__j__ Michaelis constant, or
½(Vmax) |
| n. twist |
__o__ two bases in a basepair exist out
of
plane with respect to each other |
| o. propeller twist |
__a__ rise per base 3.4 Å, 10 to
10.5
basepairs per turn, basepair tilt of 4deg, helix is elongated and
asymmetric |
26. True or False
[15 pts]
__F___ Km occurs at lower [S]
for
a competitive inhibitor
__F___ A substrate binds a
protein with high affinity forming a low energy and stable complex
__F___ A change in pH will have
no effect on enzyme activity
__T___ A DNA duplex with a
greater %GC content, will have a higher melting temperature than a
duplex of the same length with higher %AT content
__T___ a-helix, g-turn and
b-strand are all examples of protein secondary structure
__T___ Enzymes increase the
reaction rate by increasing the lifetime of the transition state.
___F__ Mutating any amino acid
in
a protein will always destroy its biological function
__T___ Base-stacking is the
dominant means of intra-strand stabilization
__T___ The hydrophobic effect is
based on the concept that a thermodynamic driving force is associated
with greasy surfaces attempting to minimize surface area that directly
contacts water
___T__ Hydrogen bonding provides
no net enthalpic contribution to protein folding
____F_ Prosthetic groups
undergo chemical modification by enzymes
__F___ Allosteric effectors do
not affect the Km, but usually change Vmax
__T___ Induced fit mechanisms
are
a component of the binding free energy
__F___ 6M Guanidinium
hydrochloride will fully oxidize cysteines
__F___ A kinase removes and a
phosphorylase adds a phosphate group to a protein