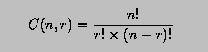
The combinatorial coefficient C(n,r) is defined as follows:
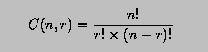
where 0 <= r <= n must hold. Write a program that keeps reading in
values for n and r, exits if both values are zeros,
uses a LOGICAL function to test if 0 <= r <= n holds,
and computes C(n,r) with an INTEGER function.
![]()
! ---------------------------------------------------------------
! This program computes the combinatorial coefficient C(n,r):
!
! n!
! C(n,r) = -------------
! r! x (n-r)!
!
! It asks for two integers and uses Cnr(n,r) to compute the value.
! If 0 <= r <= n does not hold, Cnr() returns -1 so that the main
! program would know the input values are incorrect. Otherwise,
! Cnr() returns the desired combinatorial coefficient.
!
! Note that if the input values are zeros, this program stops.
! ---------------------------------------------------------------
PROGRAM Combinatorial
IMPLICIT NONE
INTEGER :: n, r, Answer
DO
WRITE(*,*)
WRITE(*,*) "Two integers n and r (0 <= r <= n) please "
WRITE(*,*) "0 0 to stop --> "
READ(*,*) n, r
IF (n == 0 .AND. r == 0) EXIT
WRITE(*,*) "Your input:"
WRITE(*,*) " n = ", n
WRITE(*,*) " r = ", r
Answer = Cnr(n, r)
IF (Answer < 0) THEN
WRITE(*,*) "Incorrect input"
ELSE
WRITE(*,*) " C(n,r) = ", Answer
END IF
END DO
CONTAINS
! ---------------------------------------------------------------
! INTEGER FUNCTION Cnr(n,r)
! This function receives n and r, uses LOGICAL function Test()
! to verify if the condition 0 <= r <= n holds, and uses
! Factorial() to compute n!, r! and (n-r)!.
! ---------------------------------------------------------------
INTEGER FUNCTION Cnr(n, r)
IMPLICIT NONE
INTEGER, INTENT(IN) :: n, r
IF (Test(n,r)) THEN
Cnr = Factorial(n)/(Factorial(r)*Factorial(n-r))
ELSE
Cnr = -1
END IF
END FUNCTION Cnr
! ---------------------------------------------------------------
! LOGICAL FUNCTION Test()
! This function receives n and r. If 0 <= r <= n holds, it
! returns .TRUE.; otherwise, it returns .FALSE.
! ---------------------------------------------------------------
LOGICAL FUNCTION Test(n, r)
IMPLICIT NONE
INTEGER, INTENT(IN) :: n, r
Test = (0 <= r) .AND. (r <= n)
END FUNCTION Test
! ---------------------------------------------------------------
! INTEGER FUNCTION Factorial()
! This function receives a non-negative integer and computes
! its factorial.
! ---------------------------------------------------------------
INTEGER FUNCTION Factorial(k)
IMPLICIT NONE
INTEGER, INTENT(IN) :: k
INTEGER :: Ans, i
Ans = 1
DO i = 1, k
Ans = Ans * i
END DO
Factorial = Ans
END FUNCTION Factorial
END PROGRAM Combinatorial
Click here to download this program.
In the sample output above, please note the error messages indicating that condition 0 <= r <= n does not hold. Please also note that the program stops when the input values are 0 and 0.Two integers n and r (0 <= r <= n) please 0 0 to stop --> 10 4 Your input: n = 10 r = 4 C(n,r) = 210 Two integers n and r (0 <= r <= n) please 0 0 to stop --> 7 6 Your input: n = 7 r = 6 C(n,r) = 7 Two integers n and r (0 <= r <= n) please 0 0 to stop --> 4 8 Your input: n = 4 r = 8 Incorrect input Two integers n and r (0 <= r <= n) please 0 0 to stop --> -3 5 Your input: n = -3 r = 5 Incorrect input Two integers n and r (0 <= r <= n) please 0 0 to stop --> 0 0