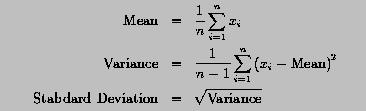
WARNING: This example assumes spaces are ignored for the I and F descriptors and the output is sent to a printer.
The mean, variance and standard deviation of a set of data can be computed with the following formulas:
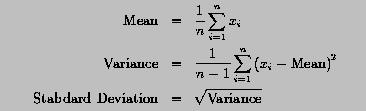
Write a program to read in a set of real values and use the above formulas to compute the mean, variance and standard deviation. Moreover, this program should generate a table containing the following addition information:
1 1 2 2 3 3 4
....5....0....5....0....5....0....5....0
Input Data:
No Data
=== ======
1 6.60
2 6.00
3 4.00
:
:
:
10 5.20
Mean : 6.7100000
Variance : 3.3498888
Standard Deviation : 1.8302702
Analysis Table:
No Data Dev
=== ====== =====
1 6.60 -0.11
2 6.00 -0.71
3 4.00 -2.71 <-- Bad
4 9.00 2.29 <-- Good
5 4.50 -2.21 <-- Bad
6 7.30 0.59
7 9.50 2.79 <-- Good
8 8.00 1.29
9 7.00 0.29
10 5.20 -1.51
![]()
! --------------------------------------------------------------------
! PROGRAM MeanVariance:
! This program reads in an array and computes the mean, variance
! and standard deviation of the data stored in the array. Then, it
! displays an analysis table. If a value is greater than the value
! of (mean + standard deviation), it displays a "good". If a value
! is less than the value of (mean - standard deviation), it displays
! a "bad".
! --------------------------------------------------------------------
PROGRAM MeanVariance
IMPLICIT NONE
INTEGER, PARAMETER :: MAX_SIZE = 50 ! maximum array size
REAL, DIMENSION(1:MAX_SIZE) :: Data ! input array
REAL :: Mean, Variance, StdDev ! results
INTEGER :: n ! actual array size
INTEGER :: i ! running index
CHARACTER(LEN=40) :: TitleHeading = '(1X, A//1X, A/1X, A)'
CHARACTER(LEN=20) :: For_Data = '(I4, F7.2)'
CHARACTER(LEN=50) :: ResultFormat = '(/1X, A, F15.7/1X, A, F15.7/1X, A, F15.7/)'
CHARACTER(LEN=20) :: For_Analysis = '(I4, 2F7.2, A)'
READ(*,*) n ! read in input array
READ(*,*) (Data(i), i = 1, n)
WRITE(*,TitleHeading) "Input Data:", &
" No Data", &
"=== ======"
WRITE(*,For_Data) (i, Data(i), i = 1, n)
Mean = 0.0 ! compute mean
DO i = 1, n
Mean = Mean + Data(i)
END DO
Mean = Mean / n
Variance = 0.0 ! compute variance
DO i = 1, n
Variance = Variance + (Data(i) - Mean)**2
END DO
Variance = Variance / (n - 1)
StdDev = SQRT(Variance) ! compute standard deviation
WRITE(*,ResultFormat) "Mean : ", Mean, &
"Variance : ", Variance, &
"Standard Deviation : ", StdDev
WRITE(*,TitleHeading) "Analysis Table:", &
" No Data Dev ", &
"=== ====== ====="
DO i = 1, n
IF (Data(i) > Mean + StdDev) THEN
WRITE(*,For_Analysis) i, Data(i), Data(i) - Mean, " <-- Good"
ELSE IF (Data(i) < Mean - StdDev) THEN
WRITE(*,For_Analysis) i, Data(i), Data(i) - Mean, " <-- Bad"
ELSE
WRITE(*,For_Analysis) i, Data(i), Data(i) - Mean
END IF
END DO
END PROGRAM MeanVariance
Click here to download this program.
The output of the program is:10 6.6 6.0 4.0 9.0 4.5 7.3 9.5 8.0 7.0 5.2
1 1 2 2 3 3 4
....5....0....5....0....5....0....5....0
Input Data:
No Data
=== ======
1 6.60
2 6.00
3 4.00
4 9.00
5 4.50
6 7.30
7 9.50
8 8.00
9 7.00
10 5.20
Mean : 6.7100000
Variance : 3.3498888
Standard Deviation : 1.8302702
Analysis Table:
No Data Dev
=== ====== =====
1 6.60 -0.11
2 6.00 -0.71
3 4.00 -2.71 <-- Bad
4 9.00 2.29 <-- Good
5 4.50 -2.21 <-- Bad
6 7.30 0.59
7 9.50 2.79 <-- Good
8 8.00 1.29
9 7.00 0.29
10 5.20 -1.51
1 1 2 2 3 3 4
....5....0....5....0....5....0....5....0
Input Data:
No Data
=== ======
The report title Input Data: and table headings
No and Data can be incorporated into a single
format.
CHARACTER(LEN=40) :: TitleHeading = '(1X, A//1X, A/1X, A)'
WRITE(*,TitleHeading) "Input Data:", &
" No Data", &
"=== ======"
As you can see, we just pull all formats together into a single
one. The title Title Data: is printed with
1X,A. The blank line between the title and the table
heading is generated by //. Then, both
No Data and === ===== are
printed with 1X,A.
1 1 2 2 3 3 4
....5....0....5....0....5....0....5....0
Input Data:
No Data
=== ======
Analysis Table:
No Data Dev
=== ====== =====
While the second table has three columns, the column heading is
simply a CHARACTER string and as a result can be printed
with 1X,A.
1 1 2 2 3 3 4
....5....0....5....0....5....0....5....0
Mean : 6.7100000
Variance : 3.3498888
Standard Deviation : 1.8302702
Each line has a format of A for printing the description
followed by F15.7 for printing the result. Note that
there is a blank line above and below these results and hence
slashes are used. This is the following format and WRITE:
CHARACTER(LEN=50) :: ResultFormat = '(/1X, A, F15.7/1X, A, F15.7/1X, A, F15.7/)'
WRITE(*,ResultFormat) "Mean : ", Mean, &
"Variance : ", Variance, &
"Standard Deviation : ", StdDev
In this way, we do not even use WRITE(*,*) for generating
blank lines! From this example, you should be able to see the
power of the slash edit descriptor.