Things to know - Chapters 3, 5, 6 & 7
MA2321, Fall '03, T. Olson
Know these terms and relationships between them:
- determinant
- triangular matrix
- diagonal matrix
- transpose
- inverse
- eigenvalue
- eigenvector
- eigenspace
- characteristic polynomial
- characteristic equation
- multiplicity
- similar matrices
- diagonalizable, diagonalization
- dot product, inner product
- orthogonal, perpendicular (vectors)
- length, norm (vector)
- distance (between vectors)
- row space, column space, nullspace
- orthogonal complement
- orthogonal matrix
- orthogonally diagonalizable
- symmetric matrix
- quadratic form
Things to think about:
- 1.
- How does each elementary row operation affect the determinant
of a matrix?
- 2.
- How do you compute determinants by hand for a
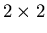 matrix?
...for a triangular matrix? ...using row reduction?
matrix?
...for a triangular matrix? ...using row reduction?
- 3.
- What's the geometrical meaning of a determinant
(in 2-D or 3-D)?
- 4.
- How is the determinant of a matrix A related to the determinant
of AT? ...of A-1? ...of AB?
- 5.
- What does it say about A if
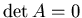 ?
?
- 6.
- What is an eigenvector?
- 7.
- For a given matrix A, how do you decide if a given number
is an eigenvalue of A?
- 8.
- For a given matrix A, how do you decide if a given vector
is an eigenvector of A?
How do you find the corresponding eigenvalue?
- 9.
- Can zero be an eigenvalue? Can the zero vector be an
eigenvector?
- 10.
- Given a matrix A and one eigenvalue of A, how do you compute
the eigenspace associated with that eigenvalue?
- 11.
- How does row reduction affect eigenvalues?
- 12.
- What does it mean if zero is an eigenvalue of a matrix?
- 13.
- What does it mean if two matrices are similar? What can you
say about the eigenvalues, eigenvectors, and/or characteristic
equations of two similar matrices?
- 14.
- How is the characteristic polynomial related to the eigenvalues?
- 15.
- How do you diagonalize a matrix (find the ``P'' and ``D''
in the factorization
A=P D P-1)? Under what conditions
can you do this?
When can you do this with an orthogonal P?
- 16.
- How do you tell if two vectors are orthogonal?
...if a set
of vectors is orthogonal?
- 17.
- What is meant by ``the orthogonal complement of W''?
If
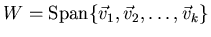 ,
how can you tell if a given vector is in
,
how can you tell if a given vector is in 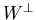 ?
?
- 18.
- What is an ``orthogonal matrix''? What is its inverse?
- 19.
- Suppose a non-square matrix U has orthonormal columns.
What do you know about UT U? ...about U UT?
- 20.
- Suppose a square matrix U has orthonormal columns.
What do you know about UT U? ...about U UT?
- 21.
- What properties are conserved under transformation
by a matrix with orthonormal columns?
- 22.
- How do you compute the projection of an arbitrary vector
onto a subspace
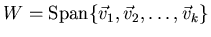 ?
(Give at least two answers, one assuming that the
?
(Give at least two answers, one assuming that the 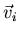 s are
orthonormal, and one assuming that they are only orthogonal).
s are
orthonormal, and one assuming that they are only orthogonal).
- 23.
- What is meant by ``the vector in
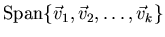 which is closest to y''? How would you compute it?
How would you check your answer using a dot product?
which is closest to y''? How would you compute it?
How would you check your answer using a dot product?
- 24.
- How can you split a given vector into the sum of two pieces:
one vector in W and one vector in
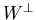 ?
?
- 25.
- Given an orthogonal basis for
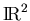 (or
(or
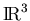 )
and an
arbitrary vector
)
and an
arbitrary vector 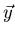 in
in
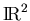 (or
(or
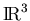 ), how
would you compute the coefficients needed to write
), how
would you compute the coefficients needed to write 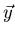 as a linear combination of the basis vectors?
as a linear combination of the basis vectors?
- 26.
- How can you tell at a glance if a given matrix is
orthogonally diagonalizable?
- 27.
- What are the special properties of symmetric matrices?
- 28.
- Given a quadratic form, how do you find a symmetric matrix A to write the quadratic form as xT A x?
If you were given A, what is the associated quadratic form?
- 29.
- How do you find a change of variables to eliminate the cross terms
in a quadratic form?
About this document ...
Tamara R. Olson
trolson at mtu.edu