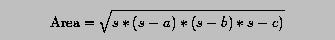
Given a triangle with side lengths a, b and c, its area can be computed using the Heron's formula:
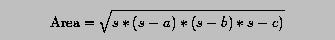
where s is the half of the perimeter length:
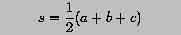
In order for a, b and c to form a triangle, two conditions must be satisfied. First, all side lengths must be positive:
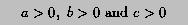
Second, the sum of any two side lengths must be greater than the third side length:

Write a program to read in three real values and use a function for testing
the conditions and another function for computing the area. Should the
conditions fail, your program must keep asking the user to re-enter the
input until the input form a triangle. Then, the other function is used
to compute the area.
![]()
! --------------------------------------------------------------------
! This program uses Heron's formula to compute the area of a
! triangle. It "contains" the following functions;
! (1) LOGICAL function TriangleTest() -
! this function has three real formal arguments and tests
! to see if they can form a triangle. If they do form a
! triangle, this function returns .TRUE.; otherwise, it
! returns .FALSE.
! (2) REAL function TriangleArea() -
! this functions has three real formal arguments considered
! as three sides of a triangle and returns the area of this
! triangle.
! --------------------------------------------------------------------
PROGRAM HeronFormula
IMPLICIT NONE
INTERFACE
LOGICAL FUNCTION TriangleTest(a, b, c)
REAL, INTENT(IN) :: a, b, c
END FUNCTION TriangleTest
REAL FUNCTION Area(a, b, c)
REAL, INTENT(IN) :: a, b, c
END FUNCTION Area
END INTERFACE
REAL :: a, b, c, TriangleArea
DO
WRITE(*,*) 'Three sides of a triangle please --> '
READ(*,*) a, b, c
WRITE(*,*) 'Input sides are ', a, b, c
IF (TriangleTest(a, b, c)) EXIT ! exit if not a triangle
WRITE(*,*) 'Your input CANNOT form a triangle. Try again'
END DO
TriangleArea = Area(a, b, c)
WRITE(*,*) 'Triangle area is ', TriangleArea
END PROGRAM HeronFormula
! --------------------------------------------------------------------
! LOGICAL FUNCTION TriangleTest() :
! This function receives three REAL numbers and tests if they form
! a triangle by testing:
! (1) all arguments must be positive, and
! (2) the sum of any two is greater than the third
! If the arguments form a triangle, this function returns .TRUE.;
! otherwise, it returns .FALSE.
! --------------------------------------------------------------------
LOGICAL FUNCTION TriangleTest(a, b, c)
IMPLICIT NONE
REAL, INTENT(IN) :: a, b, c
LOGICAL :: test1, test2
test1 = (a > 0.0) .AND. (b > 0.0) .AND. (c > 0.0)
test2 = (a + b > c) .AND. (a + c > b) .AND. (b + c > a)
TriangleTest = test1 .AND. test2 ! both must be .TRUE.
END FUNCTION TriangleTest
! --------------------------------------------------------------------
! REAL FUNCTION Area() :
! This function takes three real number that form a triangle, and
! computes and returns the area of this triangle using Heron's formula.
! --------------------------------------------------------------------
REAL FUNCTION Area(a, b, c)
IMPLICIT NONE
REAL, INTENT(IN) :: a, b, c
REAL :: s
s = (a + b + c) / 2.0
Area = SQRT(s*(s-a)*(s-b)*(s-c))
END FUNCTION Area
Click here to download this program.
Three sides of a triangle please --> -3.0 4.0 5.0 Input sides are -3., 4., 5. Your input CANNOT form a triangle. Try again Three sides of a triangle please --> 1.0 3.0 4.0 Input sides are 1., 3., 4. Your input CANNOT form a triangle. Try again Three sides of a triangle please --> 6.0 8.0 10.0 Input sides are 6., 8., 10. Triangle area is 24.
INTERFACE
LOGICAL FUNCTION TriangleTest(a, b, c)
REAL, INTENT(IN) :: a, b, c
END FUNCTION TriangleTest
REAL FUNCTION Area(a, b, c)
REAL, INTENT(IN) :: a, b, c
END FUNCTION Area
END INTERFACE